Content
- Introduction to Distributed Systems
- Architecture of the Distributed Systems
- Communication in Distributed Systems
Distributed Systems VS Distributed computing
A distributed system is a network that consists of autonomous computers that are connected using a distribution middle ware. Furthermore They help in sharing different resources and capabilities to provide users with a single and integrated coherent network.
The key features of a distributed system are,
- Components in the system are concurrent moreover a distributed system allows resource sharing, including software by systems connected to the network at the same time.
- They will generally be autonomous in nature, but there can be multiple components.
- A global clock is not required in a distributed system. So that the systems can be spread across different geographies.
- There is greater fault tolerance in a distributed model than other models.
- Price/performance ratio is much better.
The key goals of a distributed system:
- Transparency:Achieving the image of a single system image without concealing the details of the location, access, migration, concurrency, failure, relocation, persistence and resources to the users
- Openness: Making the network easier to configure and modify
- Reliability: Compared to a single system, a distributed system should be highly capable of being secure, consistent and have a high capability of masking errors.
- Performance: Compared to other models, distributed models are expected to give a much-wanted boost to performance.
- Scalability: Distributed systems should be scalable with respect to geography, administration or size.
Challenges for distributed systems include:
- Security is a big challenge in a distributed environment, especially when using public networks.
- Fault tolerance could be tough when the distributed model is built based on unreliable components.
- Coordination and resource sharing can be difficult if proper protocols or policies are not in place.
- Process knowledge should be put in place for the administrators and users of the distributed model.
Distributed computing is a model in which components of a software system are shared among multiple computers in order to improve efficiency and performance. Furthermore according to the narrowest of definitions, distributed computing is limited to programs with components shared among computers within a limited geographic area.
field of computer science that studies distributed systems is Distributed computing .A distributed system is a system whose components are located on different networked computers and passing messages to one another to communicate and coordinate their actions.
Standalone Systems
Standalone. A Standalone application is a binary that can be launched directly. That is, it does not run on the Streams runtime environment. You can instruct the compiler to generate a Standalone application by providing the -T option at compile time. In Standalone mode, all operators will be fused into a single partition and a single processing element (PE) will be generated for this partition. A Standalone executable is also generated with the name Standalone in the output/bin directory. When launched, this executable will load the aforementioned PE.
A standalone device is any mechanism or system that can perform its function without the need of another device, computer, or connection. Moreover a perfect example of a standalone device is a copy of a fax machine.
Advantages VS Disadvantages of Standalone systems

Standalone Systems vs Distributed Systems.

Examples of distributed systems and applications of distributed computing,
- telecommunication networks – telephone networks and cellular networks,
- network applications – World Wide Web and peer-to-peer networks,
- real-time process control – aircraft control systems,
- parallel computation
Characteristics of a web based system,
The characteristics of a web application are many and varied in comparison to traditional applications. Furthermore there is a larger spectrum of possibilities for each web application characteristic. An additional motivation to examine a web application’s usability is provided by these differences .Through determining of the set of usability attribute, these characteristics can aide in better defining and measuring web usability.
Micro service architecture ,
Micro services are a software development technique—a variant of the service-oriented architecture (SOA) architectural style that structures an application as a collection of loosely coupled services. In a micro services architecture, servicesare fine-grained and the protocols are lightweight.
Monolithic architecture,
Monolithic, in this context, means composed all in one piece. Monolithic software is designed to be self-contained; components of the program are interconnected and interdependent rather than loosely coupled as is the case with modular software programs.
Monolithic architecture vs Micro service Architecture,

The characteristics of a web application are many and varied in comparison to traditional applications. Furthermore there is a larger spectrum of possibilities for each web application characteristic. To examine a web application’s usability, these differences provide additional motivation . Moreover through determining of the set of usability attribute, these characteristics can aide in better defining and measuring web usability.
MVC style,
The MVC design pattern decouples these major components allowing for efficient code reuse and parallel development and traditionally used for desktop graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Moreover this architecture has become popular for designing web applications and even mobile, desktop and other clients.
Faster development process – MVC supports rapid and parallel development. then it is possible that one programmer can work on the view while the another can work on the controller to create business logic of the web application, If an MVC model is used to develop any particular web application .
Furthermore Model View Controller or MVC , is a software design pattern for developing web applications. A Model View Controller pattern is made up of the following three parts − Model − The lowest level of the pattern which is responsible for maintaining data.
In object-oriented programming development, model-view-controller (MVC) is the name of a methodology or design pattern for successfully and efficiently relating the user interface to underlying data models. The MVC pattern is widely used in program development with programming languages such as Java, Smalltalk, C, and C++.
The MVC pattern has been heralded by many developers as a useful pattern for the reuse of object code and a pattern that allows them to significantly reduce the time it takes to develop applications with user interfaces.
Moreover the Model-View-Controller (MVC) is an architectural pattern that separates an application into three main logical components which are the model, the view, and the controller. Each of these components are built to handle specific development aspects of an application.
- A Model , which represents the underlying, logical structure of data in a software application and the high-level class associated with it. This object model does not contain any information about the user interface.
- A View , which is a collection of classes representing the elements in the user interface (all of the things the user can see and respond to on the screen, such as buttons, display boxes, and so forth)
- A Controller , which represents the classes connecting the model and the view, and is used to communicate between classes in the model and view.
Advantages VS Disadvantages of MVC ,

RPC
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is a protocol that one program can use to request a service from a program located in another computer on a network without having to understand the network’s details. Moreover A procedure call is also sometimes known as a function call or a subroutine call.
RMI
- Remote Method Invocation (RMI)
- Understanding stub and skeleton
- stub
- skeleton
- Requirements for the distributed applications
- Steps to write the RMI program
- RMI Example
The RMI (Remote Method Invocation) is an API that provides a mechanism to create distributed application in java which allows an object to invoke methods on an object running in another JVM.
The RMI provides remote communication between the applications using two objects stub and skeleton.
CORBA,
WHAT IS CORBA?
CORBA® is the acronym for Common Object Request Broker Architecture™, OMG®’s open, vendor-independent architecture and infrastructure that computer applications use to work together over networks.
WHAT IS CORBA GOOD FOR?
CORBA is useful in many situations. CORBA works behind the scenes in the computer rooms of many of the world’s largest websites, ones that you probably use every day.
CORBA STANDARDS
OMG’s best support for server-side scalability comes from the CORBA Component Model. Moreover over 400 attendees at each OMG meeting make it a happening as well as an occasion to advance the OMG specification suite.
XML
XML. Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. The W3C’s XML 1.0 Specification and several other relatedspecifications—all of them free open standards—define XML.Type of format: Markup languageUniform Type Identifier (UTI): public.xmlOpen format?: YesExtended from: SGML
JSON VS XML
Why JSON Is Better Than XML. For awhile, XML (extensible markup language) was the only choice for open data interchange. But over the years there has been a lot of transformation in the world of open data sharing.
The more lightweight JSON (Javascript object notation) has become a popular alternative to XML for various reasons. Some are;
- Less verbose- XML uses more words than necessary
- JSON is faster- Parsing XML software is slow and cumbersome. Many of these DOM manipulation libraries can lead to your applications using large amounts of memory due to the verbosity and cost of parsing large XML files.
XML:
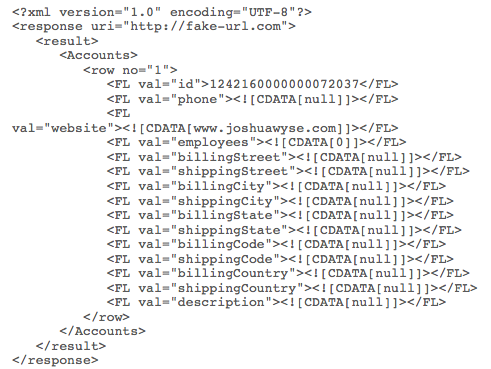
This XML structure is not intuitive, making it hard to represent in code.
JSON:

JSON’s structure is intuitive, making it easy to read and map directly to domain objects in whatever programming language is being used.
benefits of JSON over XML
- JSON data model’s structure matches the data – JSON’s data structure is a map whereas XML is a tree. Although a map (just key/value pairs) can be limiting, that’s what we want, because it is easier to interpret and is predictable.
- In code – Items are represented the same way in code. In many languages, especially dynamic ones, you can just ‘slurp in the JSON’ and you immediately have your domain object. It is easy to go from objects in JSON to the objects in code because they align. When going from objects in XML to objects in code they do not align and there is a lot of room for interpretation.
- JSON is limiting, but that’s a good thing – JSON is limited in terms of what objects can be modeled. Some may think XML is better because more objects can be modeled and it doesn’t prohibit developers. But even though JSON prohibits developers, it is in a positive way, making the code simpler, more predictable, and easy to read. XML can be formatted to look and function any way a company wants, but it makes it difficult for developers to read, understand, and convert. In most cases people believe XML is better because developers can do anything under the sun but in the age of simplifying, less is more, making JSON a better alternative.
Building RESTful APIs as Cloud Elements does, requires a reliable, fast, and easy to use form of data exchange. Furthermore all of our APIs use JSON, and for endpoints that don’t support JSON, we transform our easy-to-understand JSON into XML and back, so you don’t have to deal with it. As RESTful API practices and simpler forms of data exchange become more popular, JSON will be leaving XML practices in the dust.
Apache Ant and Maven
Differences

Group ID,Artifact ID, Version & Packaging
group Id uniquely identifies your project across all projects, so we need to enforce a naming schema. Moreover a group Id must follow Java’s package name rules. This means it must start with a reversed domain name you control. You can create as many subgroups as you want.
artifact Id is the name of the jar without version.
Packaging
The products of Maven are always written to the “target” directory. ” mvn clean will erase these products, so generally build a package using the command “mvn clean package”. Moreover “packaging jar” means quite simply that the goal is to produce a jar file in the target directory. ” packaging war” would build a WAR file.
Version
SNAPSHOT is a special version that indicates a current development copy. Unlike regular versions, Maven checks for a new SNAPSHOT version in a remote repository for every build.